|
| Hip FracturesSymptoms of a Hip Fracture
Risks and Causes of a Hip Fracture
Tests for Hip FracturesYour doctor will perform a physical exam and request an x-ray to diagnose a hip fracture and determine the type of treatment that you need. Your doctor may do an MRI to see if there is additional damage to the soft tissue of the hip that requires treatment. Surgical ProceduresHip fractures almost always require surgery. The type of surgery will depend on the severity and location of the fracture as well as the age of the patient. A hip replacement may be performed with patients over 60 years of age who are less active. Historically, hip replacements have tended to wear out in more active patients so were generally avoided in young people and more active elderly patients. Hip replacements (both the components and the surgeries) are getting better on a continual basis, and are becoming a more viable option to patients that would not have been well served by such a replacement in the past. Femoral Neck Fractures of the Hip - Hip Pinning SurgeryIf the surgeon opted NOT to do a hip replacement for a patient with a fracture in the femoral neck, the patient will most likely undergo "hip pinning". Hip pinning involves placing several screws across the fractured femoral head, and is usually only done in younger patients, or if the fractured bones are well aligned. Even when this procedure is done properly, a partial or full hip replacement may be necessary in the future. Hip pinning is basically intracapsular repair (see image below for reference) Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures- Metal Plate SurgeryIntertrochanteric hip fractures are usually repaired with surgery by adhering a metal plate to the shaft of the femur with several small screws. X-rays are used to get the proper alignment, and then an 3" incision is made. The surgeon will affix the metal plate along the length of the fracture, and secure it with screws. 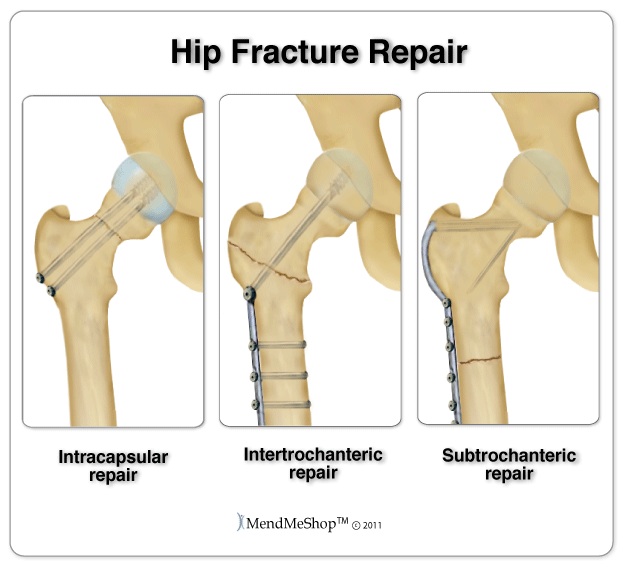 Hip HemiarthroplastyHip hemiarthroplasty is a term that describes a partial hip replacement. The surgeon removes the femoral head and replaces it with a metal "ball" that will sit in the hip socket. This procedure is required when the hip fracture is especially mis-aligned or severely fractured. Treating a Hip FractureIn case you were not sure, a hip fracture is a serious medical emergency! Immediate treatment is necessary, so get to the hospital quickly. With a hip fracture, it is pretty much a given that you will be undergoing surgery. Significant secondary damage will probably have occurred from the fracture, including complications to nearby nerves, blood vessels and protective cartilage in the joint. Most probably, the ligaments surrounding the hip joint will have been damaged - perhaps strained or even ruptured. All of these issues will determine the length of your rehabilitation. In some cases, damage to blood vessels near the hip joint can cause a loss of blood supply to the bone - this is known as osteonecrosis.
In nearly all cases of post fracture recovery, your physician, physical therapist or surgeon will recommend a treatment recovery plan for you that will include Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, Stretching - basically an outline of conservative treatments. Protocols used in recovery from a hip fracture basically the same protocols found in hip post surgery recovery. View more information about post operative recovery/rehabilitation of the hip here. We've helped thousands of people treat their painful injuries and conditions to get them back on the road to a pain-free life! Click HERE to Go To Our Online Store We take all major credit cards and Paypal. Our customer service lines are open 5 days a week helping people understand their injuries and how to treat them. Simply call toll free 1-866-237-9608 to talk or place an order with one of our knowledgeable Product Advisers. They have the ability to answer questions and even put together a treatment plan for you. Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday. Learn More About Hip Joint Injuries & TreatmentsI want to learn more about Hip Surgery & Post-Surgery Recovery I want to learn more about Circulation Boost I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For The Hip? I want to learn more about Trigger Points in the Hip I want to learn more about Hip Surgery: Do I Need It? During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort at the location of your soft tissue injury until the pain and inflammation settle. Always consult your doctor and/or Physical Therapist before using any of our outstanding products, to make sure they are right for you and your condition. The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results! |
   |

